

They are synonymous if the fluid density is known. They define the flow of the fluid in various ways, i.e., how they are measured. There are two different viscosity measures used to describe fluids, dynamics and kinematic viscosities. Or it can be measured with household equipment, such as calculating how fast a liquid can travel on a slight incline after a certain period of time. Viscosity can be measured by a viscometer, a piece of equipment that measures the force necessary to move through a liquid. As you'll see in this equation, if the spere's speed is lower, the viscosity would be higher. The SI unit of viscosity is Pascal seconds (Pa s). G is the acceleration because of gravity. ?p is the density between the fluid and sphere tested, Consequently, internal friction and viscosity increase.Where η (eta) is defined as the viscosity,
KINEMATIC VISCOSITY DEFINITION WIKIPEDIA FREE
In most liquids, pressure reduces the free volume in the internal structure, and thus limits the movability of molecules. For example, lubricants in cogwheels or gears can be submitted to pressures of 1 GPa and higher.Įquation 4. Highly viscous mineral oils react with a viscosity increase of times 20000 under identical circumstances.įor synthetic oil this pressure change can even result in a viscosity increase by a factor of up to 8 million. This applies to most low-molecular liquids.

In case the pressure goes up from 0.1 MPa to 200 MPa, the viscosity can rise to 3 to 7 times the original value. For comparison: This same change in viscosity is usually provoked by a minor temperature change of 1 K (1 ☌). Most liquids react to a significantly altered pressure (from 0.1 MPa to 30 MPa) with a viscosity change of about 10 %. However, fluids are not dramatically affected if the applied pressure is low or medium: liquids are almost non-compressible in this pressure range. Normally, an increase in pressure causes a fluid’s viscosity to increase, too. Three factors determine a substance’s flow behavior. Still, shear rate is not the only influencer. To learn more consult “ The Rheology Handbook”. The flow behavior of non-Newtonian liquids can be far more complex than these basic examples. yogurt), while for others the viscosity increases with increasing shear rate (curve 3 | e.g. If its viscosity changes with the shear rate, a liquid is non-Newtonian and – for exact definition – one has to specify the apparent viscosity.ĭifferent shear-dependent fluids behave differently: For some, their viscosity decreases when the shear rate increases (curve 2 | e.g. Typical Newtonian liquids are water or salad oil. For a Newtonian liquid, this function is a straight line (curve 1) see figure 6. Such fluids are named ‘Newtonian liquids’ after Sir Isaac Newton.Ī viscosity function shows the viscosity over the shear rate. the shear rate – acting upon the fluid, it is ideally viscous. If a fluid’s internal flow resistance is independent of the external force – i.e. High-viscosity fluids resist deformation. Fluids which flow easily show a low resistance to deformation. viscous fluids that contain an elastic portion. The specific field of viscometry covers ideally viscous fluids, and – considering certain restrictions – also viscoelastic liquids, i.e.

sweet jelly) or as a viscoelastic liquid (like e.g. According to a material’s properties, we either classify it as a viscoelastic solid (like e.g.
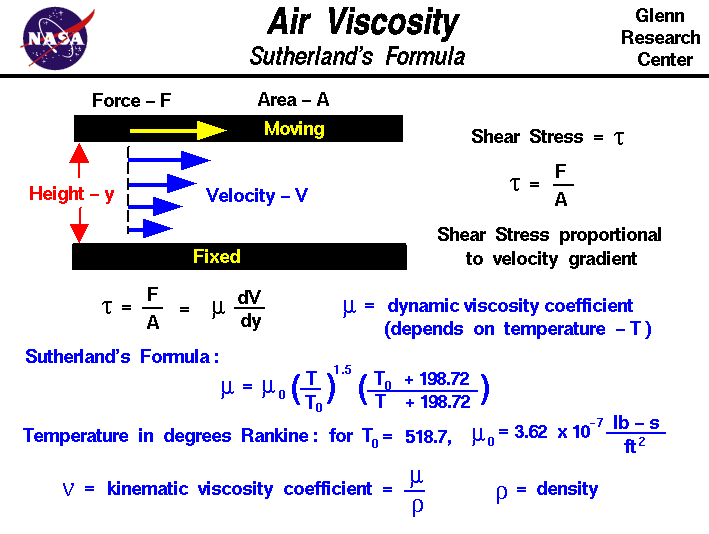
That is, substances which are neither completely elastic, nor entirely viscous. In everyday life, we mostly come across viscoelastic materials. Scientists specify solid materials as being elastic and liquids as being viscous. Imagine all materials as classified on a virtual scale from solid to liquid. Rheology deals with the flow behavior and deformation of materials. In order to determine a fluid’s viscosity, you have to enter the field of viscometry, a subject area of a wider science called rheology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
